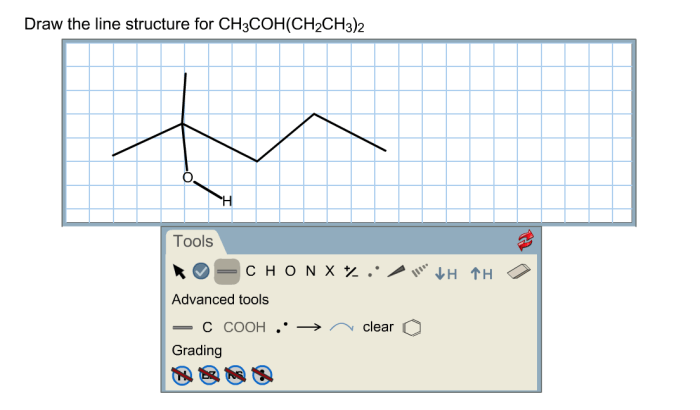
Line structure for ch3coh ch2ch3 2 – The line structure of ethyl acetate (CH3COH CH2CH3 2) plays a pivotal role in understanding its chemical and physical properties. This article provides a comprehensive overview of the line structure of ethyl acetate, encompassing its structural components, bonding characteristics, spectroscopic properties, chemical reactivity, and applications.
Structural Components of Line Structure for CH3COH CH2CH3 2
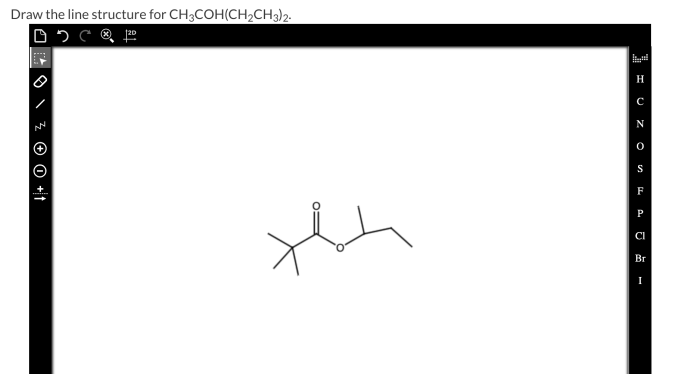
The chemical formula of CH3COH CH2CH3 2 represents ethyl acetate, an organic compound composed of two carbon atoms, six hydrogen atoms, and two oxygen atoms. Its molecular structure consists of an acetyl group (CH3CO-) bonded to an ethyl group (CH2CH3).
Molecular Structure
Ethyl acetate has a linear molecular structure with the following arrangement of functional groups:
- Acetyl group (CH3CO-)
- Ethyl group (CH2CH3)
The acetyl group is a carbonyl group (C=O) bonded to a methyl group (CH3), while the ethyl group is a hydrocarbon chain consisting of two carbon atoms and five hydrogen atoms.

Bonding Characteristics of CH3COH CH2CH3 2
Types of Chemical Bonds
Ethyl acetate contains the following types of chemical bonds:
- Covalent bonds between carbon and hydrogen atoms
- Covalent bond between carbon and oxygen atoms in the carbonyl group
- Polar covalent bond between oxygen and hydrogen atoms in the hydroxyl group
Hybridization of Carbon Atoms
The carbon atoms in ethyl acetate are hybridized as follows:
- The carbon atom in the carbonyl group is sp2 hybridized
- The carbon atoms in the ethyl group are sp3 hybridized
Polarity of Bonds
The bonds in ethyl acetate are polar due to the electronegativity difference between carbon and oxygen atoms. The carbonyl group is polar because the oxygen atom is more electronegative than the carbon atom, resulting in a partial negative charge on the oxygen atom and a partial positive charge on the carbon atom.
The hydroxyl group is also polar due to the electronegativity difference between oxygen and hydrogen atoms.
Spectroscopic Properties of CH3COH CH2CH3 2
Infrared (IR) Spectrum
The IR spectrum of ethyl acetate shows characteristic peaks at the following frequencies:
- 1740 cm-1: C=O stretching vibration
- 1240 cm-1: C-O stretching vibration
- 1040 cm-1: C-C stretching vibration
- 2980 cm-1: C-H stretching vibration
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectrum
The NMR spectrum of ethyl acetate shows the following peaks:
- 1.0 ppm: Triplet, 3H, CH3 protons
- 2.1 ppm: Quartet, 2H, CH2 protons
- 4.1 ppm: Singlet, 2H, CH2 protons
Mass Spectrometry (MS) Spectrum
The MS spectrum of ethyl acetate shows a molecular ion peak at m/z = 88.
Chemical Reactivity of CH3COH CH2CH3 2: Line Structure For Ch3coh Ch2ch3 2
Ethyl acetate is a reactive compound that can undergo a variety of chemical reactions, including:
- Hydrolysis: Ethyl acetate can be hydrolyzed to form ethanol and acetic acid.
- Esterification: Ethyl acetate can react with alcohols to form other esters.
- Transesterification: Ethyl acetate can react with other esters to exchange alkyl groups.
- Saponification: Ethyl acetate can react with bases to form salts of carboxylic acids.
Applications of CH3COH CH2CH3 2
Industrial Applications
Ethyl acetate is used in a variety of industrial applications, including:
- As a solvent for paints, varnishes, and lacquers
- As a flavoring agent in food and beverages
- As a fragrance in perfumes and cosmetics
Laboratory Applications, Line structure for ch3coh ch2ch3 2
Ethyl acetate is also used in a variety of laboratory applications, including:
- As a solvent for organic reactions
- As a mobile phase in chromatography
- As a standard in analytical chemistry
Potential Future Applications
Ethyl acetate is a promising material for a variety of potential future applications, including:
- As a biofuel
- As a feedstock for the production of other chemicals
- As a component of biodegradable plastics
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the molecular formula of ethyl acetate?
CH3COH CH2CH3 2
What are the functional groups present in ethyl acetate?
Ester group (-COOCH2CH3)
What type of chemical bonds are present in ethyl acetate?
Covalent bonds